Gum Disease Treatment
Gum Disease
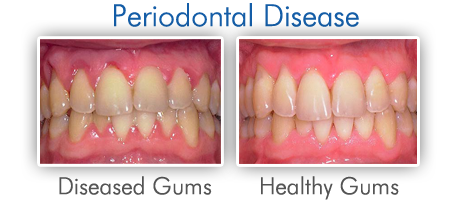
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the gums surrounding your teeth. Gum disease is one of the top reasons for tooth loss in adults. It can be virtually pain-free, therefore many patients do not know they have the disease. During each checkup, your hygienist and dentist will check for signs of periodontal disease.
What causes Gum Disease?
Gum disease is caused by a build up of plaque (a sticky form of bacteria that forms on the teeth). If the plaque is not removed (by a good oral hygiene regime such as flossing, brushing and regular professional scale and cleans), it will continue to build up and create toxins that can damage the gums. It can become hardened and form calculus (tartar) which is porous and rough and harbours even more bacteria around your teeth and gums. This calculus can only be removed by your dental professional. Periodontal disease develops just around and below the gum line. Small "pockets" that separate the gums from the teeth are then formed following this inflammation.
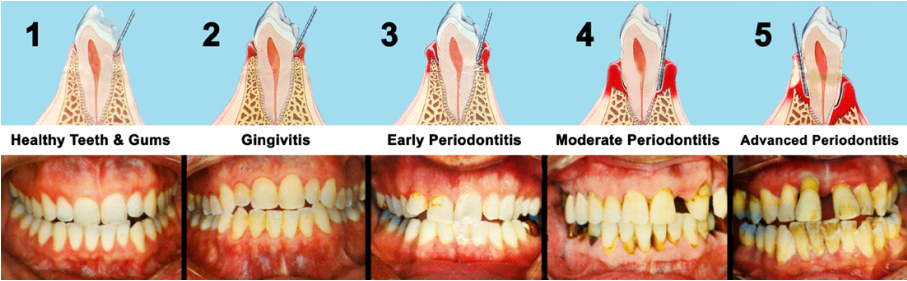
Gingivitis and periodontitis are 2 terms used for gum disease which refer to the severity of the disease.
Gingivitis and periodontitis are 2 terms used for gum disease which refer to the severity of the disease.
Gingivitis — This is the early stage of gum disease, when the gums become red and swollen, and bleed easily. At this stage, the disease is more easily treatable and can usually be eliminated by thorough daily brushing and flossing.
Periodontitis — If left untreated, gingivitis may advance to periodontitis where the surrounding tissues supporting your teeth (the gums and bone) can become seriously and irreversibly damaged. Mild, moderate and severe periodontal disease describe it's severity. Gums affected by periodontitis can cause your teeth to become loose, fall out or have be removed by a dentist. Signs of periodontal disease include bleeding gums, recession of gums - teeth appear longer, loosening of teeth.
Bad breath (halitosis) is also another sign (see below).
Periodontitis — If left untreated, gingivitis may advance to periodontitis where the surrounding tissues supporting your teeth (the gums and bone) can become seriously and irreversibly damaged. Mild, moderate and severe periodontal disease describe it's severity. Gums affected by periodontitis can cause your teeth to become loose, fall out or have be removed by a dentist. Signs of periodontal disease include bleeding gums, recession of gums - teeth appear longer, loosening of teeth.
Bad breath (halitosis) is also another sign (see below).
Factors That Can Cause Gum Disease
Certain factors can increase a person's risk of developing periodontal disease, including:
Some Signs and Symptoms
YourSmileDental Can Help You
Treatment for gum disease can vary depending on the severity of each individual case. Typical treatments include:
|